What is the Sweetener in Coke Zero
You may wonder what the sweetener in Coke Zero is. Coke Zero uses aspartame and acesulfame potassium to create a sweet taste without sugar or calories. Many people care about which sweeteners go into their drinks because health and safety matter. Recent studies show that most consumers view artificial sweeteners as harmful, and label reading remains low. This concern grows as more countries use taxes and regulations to promote healthier beverage choices. Understanding what goes into your favorite drinks helps you make better decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Coke Zero uses two artificial sweeteners, aspartame and acesulfame potassium, to provide sweetness without sugar or calories.
- Both sweeteners are approved by the FDA and considered safe when consumed within recommended daily limits.
- The blend of sweeteners helps Coke Zero taste similar to regular Coke while keeping it calorie-free.
- Using Coke Zero can help reduce sugar and calorie intake, which may support weight management and blood sugar control.
- Some people may experience side effects or prefer to limit artificial sweeteners, especially children, pregnant women, and those with health concerns.
- Moderation is important; drinking large amounts of diet sodas may carry health risks, so balance with water and healthy drinks.
- Coke Zero differs from Diet Coke by using a blend of sweeteners, giving it a bolder taste closer to classic Coke.
- Natural sweetener alternatives like stevia are available for those who want to avoid artificial sweeteners.
Sweetener in Coke Zero

Coke Zero uses a combination of two artificial sweeteners: aspartame and acesulfame potassium. Both sweeteners are approved by the FDA and are widely used in many food and beverage products. You might notice these names on the ingredient list when you check the label. The sweetener in Coke Zero helps create a taste that closely matches regular Coke, but without the sugar or calories.
Aspartame
Role
Aspartame acts as a primary sweetener in Coke Zero. It is about 180 to 200 times sweeter than regular sugar, so you only need a small amount to achieve the desired sweetness. This allows you to enjoy a sweet drink without adding calories. Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EFSA have set acceptable daily intake levels for aspartame, reflecting its safety when consumed within these limits. Aspartame is present in over 6,000 food and beverage products, showing its popularity and effectiveness.
Taste
Aspartame provides a clean, sweet flavor that many people find pleasant. Unlike older artificial sweeteners such as saccharin or cyclamate, aspartame does not leave a strong bitter aftertaste. However, its sweetness develops a bit more slowly than sugar, and some people notice a slight aftertaste. Beverage makers often combine aspartame with other sweeteners to improve the overall taste. Studies show that aspartame delivers a taste profile that works well in soft drinks, making it a key part of the sweetener in Coke Zero.
Acesulfame Potassium
Role
Acesulfame potassium, also known as Ace-K, works alongside aspartame to enhance sweetness. It is about 200 times sweeter than sugar and is stable under heat and acidic conditions, which makes it suitable for carbonated drinks. The FDA and international agencies have approved Ace-K for use in foods and beverages since the 1980s. Research shows that Ace-K does not affect blood sugar or insulin levels, so you can safely consume it even if you are concerned about glucose control.
Taste
Ace-K has a fast, sweet taste but can have a slightly bitter aftertaste when used alone. When you blend Ace-K with aspartame, the combination helps mask any bitterness and creates a more sugar-like flavor. A study using taste sensors found that the typical concentration of Ace-K in beverages like Coke Zero falls between 0.2 and 0.7 millimoles per liter. This research also shows that mixing Ace-K with other sweeteners, such as aspartame, optimizes sweetness and reduces unwanted flavors.
Blend Benefits
You benefit from the blend of aspartame and acesulfame potassium in several ways. The combination allows Coke Zero to deliver a taste that is closer to regular Coke, without the calories or sugar. Research comparing blends of these sweeteners with sugar found that people who drank the blend consumed fewer calories per meal—almost 200 calories less—than those who drank sugar-sweetened beverages. The blend does not significantly affect appetite or blood sugar, making it a smart choice if you want to reduce your calorie intake. The sweetener in Coke Zero is carefully balanced to give you a satisfying, refreshing taste while supporting your health goals.
Why Use These Sweeteners
Sugar Replacement
You might wonder why Coke Zero uses artificial sweeteners instead of sugar. The main reason is health. Large studies show that replacing sugar with artificial sweeteners in drinks can help lower the risk of type 2 diabetes. Researchers have found that people who switch from sugar-sweetened beverages to those with artificial sweeteners may see improvements in their health. Experts recommend this switch as a way to reduce disease risk, especially for people who want to manage their blood sugar or avoid extra calories. Many people choose drinks with artificial sweeteners because they want to cut down on sugar without giving up the sweet taste they enjoy.
Tip: If you want to reduce your sugar intake, choosing drinks with artificial sweeteners can be a smart step.
Calorie-Free
One of the biggest benefits of the sweetener in Coke Zero is that it adds no calories to your drink. Studies and clinical trials show that replacing sugar with artificial sweeteners leads to a real drop in daily calorie intake. This calorie reduction can help with weight management. For example, research shows that people who switch to calorie-free sweetened drinks often lose weight or keep their weight steady. Even when compared to drinking water, using artificial sweeteners in place of sugar still helps lower your total calorie intake. This makes Coke Zero a good choice if you want to enjoy a sweet soda without worrying about extra calories.
- Key benefits of calorie-free sweeteners:
- No added sugar
- No extra calories
- Support for weight control
Flavor Profile
Taste matters when you choose a drink. Coke Zero uses a blend of aspartame and acesulfame potassium to create a flavor that is very close to regular Coke. Taste tests and consumer reviews show that Coke Zero has a strong cola flavor with a bit more spice and a rounder taste than the original. Some people notice a slight difference, saying Coke Zero tastes a little flatter or has a mild artificial note. However, many agree that it is the best calorie-free option for those who want a soda that tastes similar to regular Coke. The sweetener in Coke Zero helps deliver this familiar flavor while keeping the drink sugar-free.
Note: While Coke Zero’s taste is not identical to regular Coke, most people find it a satisfying alternative with fewer sharp notes and a strong cola essence.
Safety and Approval
FDA Status
You may wonder if the sweeteners in your drinks are safe. The FDA has approved both aspartame and acesulfame potassium for use in foods and beverages. These approvals come after careful review of scientific data. The FDA has examined over 100 studies on aspartame and more than 90 studies on Ace-K. These studies cover toxicology, metabolism, cancer risk, and effects on reproduction. Health Canada, the European Food Safety Authority, and other international agencies agree with the FDA’s findings. They have set acceptable daily intake levels for both sweeteners. These limits help protect your health and ensure you can safely enjoy products like Coke Zero. The FDA continues to monitor new research and updates its guidance as needed.
Scientific Consensus
Scientists have studied aspartame and Ace-K for decades. Aspartame alone has been the subject of over 1,000 scientific publications since 2000. Most experts agree that these sweeteners are safe when you consume them within the recommended limits. The World Health Organization and the International Agency for Research on Cancer recently classified aspartame as “possibly carcinogenic.” This label means there is limited evidence, not a proven risk. The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives reaffirmed that aspartame is safe at levels up to 40 mg per kilogram of body weight per day. The FDA and other agencies also confirm that the sweetener in Coke Zero does not pose a safety concern when used as directed. These sweeteners help you manage your calorie intake and blood sugar, which can lower your risk for obesity and diabetes.
Common Concerns
You may have heard about possible health risks linked to artificial sweeteners. Researchers continue to study these questions. Some peer-reviewed studies report a small increase in certain cancer risks with as high as aspartame intake. For example, one study found a 22% higher risk of breast cancer and a 15% higher risk of obesity-related cancers among heavy consumers. Other large studies have linked frequent consumption of artificially sweetened drinks to higher risks of stroke, heart disease, and even death from any cause. These risks appear stronger in people who drink two or more diet sodas daily, especially those who are obese.
- Some studies suggest artificial sweeteners may:
- Increase sugar cravings and appetite
- Affect gut bacteria and glucose tolerance
- Raise the risk of type 2 diabetes and weight gain
- Influence hunger signals in the brain
Note: Most of these studies show associations, not direct cause and effect. Short-term clinical trials sometimes show benefits, such as weight loss, when you replace sugar with artificial sweeteners. However, researchers still debate the long-term effects. You should stay informed and consider moderation when choosing drinks with artificial sweeteners.
Health Effects
Blood Sugar
You may wonder how artificial sweeteners in Coke Zero affect your blood sugar. Many people choose these drinks to avoid spikes in glucose. Clinical trials have shown mixed results. Some studies found that certain sweeteners, like sucralose, can increase insulin levels after you drink them. For example, one trial showed a 20% rise in insulin when people consumed sucralose before a glucose test. Other research suggests that artificial sweeteners might change your gut microbiome, which could affect how your body handles sugar. In some cases, these changes led to higher blood sugar levels and reduced glucose tolerance. However, not all studies agree. Large reviews of clinical trials have found no consistent effect on fasting blood sugar or insulin resistance. No randomized controlled trials have directly tested whether these sweeteners cause type 2 diabetes, but some long-term studies link higher intake to increased diabetes risk. The science is still evolving, so you should stay informed and watch for new research.
Tip: If you have diabetes or concerns about blood sugar, talk to your doctor before making changes to your diet.
Weight
Many people drink Coke Zero to help manage their weight. You might expect that swapping sugar for artificial sweeteners would help you lose pounds. Some clinical trials support this idea. People who switch to low-calorie sweetened drinks often see weight loss or maintain their weight. However, long-term studies tell a more complex story. Research tracking thousands of people over several years found that those who drank more artificially sweetened beverages often gained more weight and had larger waistlines. For example, one study followed older adults for almost a decade and found greater increases in waist size among diet soda drinkers. Meta-analyses also show a small but measurable link between artificial sweetener use and higher body mass index (BMI). Scientists think this may happen because some people eat more calories later to make up for the “saved” calories, or because sweeteners affect hunger signals.
| Study Type | Key Finding |
|---|---|
| Prospective cohort study | Diet beverage consumers had greater increases in waist circumference over 9.4 years. |
| Meta-analysis | Artificial sweetener intake is linked to a modest increase in BMI (0.03 kg/m²). |
| Large cohort study | Daily consumers had 0.77 kg/m² higher BMI than non-consumers over 8 years. |
Side Effects
You may also want to know about the possible side effects of artificial sweeteners. Some people report headaches, digestive issues, or changes in taste after drinking diet sodas. Large studies have linked higher intake of sweeteners like aspartame and acesulfame potassium to increased risks of type 2 diabetes and heart disease. For example, a French study with over 100,000 adults found that people who consumed more artificial sweeteners had a higher risk of developing diabetes, even after accounting for weight and sugar intake. Other research suggests a possible link to heart disease and stroke, but these findings are not always consistent. Many factors, such as lifestyle and diet, can affect these results. Most health agencies consider these sweeteners safe when you use them within recommended limits, but you should pay attention to how your body responds.
Note: If you notice side effects after drinking Coke Zero, consider reducing your intake or choosing other beverages.
Who Should Avoid
You may wonder if everyone can safely drink Coke Zero or other beverages with artificial sweeteners. While most healthy adults can enjoy these drinks in moderation, some groups should use extra caution or avoid them altogether.
Experts often recommend that children limit or avoid artificial sweeteners. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the Institute of Medicine both suggest that these sweeteners should not make up a significant part of a child’s diet. Children need nutrients from milk, juice, and whole foods to grow and develop. If you give a child drinks with artificial sweeteners, they might drink less of these nutritious options. Some studies also raise concerns about possible effects on body fat and heart health in children, but the results are mixed. Because of these uncertainties, health organizations urge parents to be careful and choose drinks with natural sugars or water for kids.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women also face special considerations. Scientists do not have enough long-term data on the safety of artificial sweeteners for these groups. Some sweeteners can pass through the placenta or into breast milk. The effects on a developing baby or a nursing infant remain unclear. For this reason, many doctors and nutritionists suggest that you avoid or limit artificial sweeteners during pregnancy and breastfeeding. This approach follows the precautionary principle, which means you should act carefully when the science is not settled.
If you have diabetes, you may look to artificial sweeteners as a way to manage your blood sugar. Most research shows that sweeteners like aspartame and acesulfame potassium do not raise blood sugar levels when used within the acceptable daily intake. You can use them as part of a plan to reduce sugar and calories. However, long-term studies are still limited. You should talk to your doctor or dietitian before making big changes to your diet.
Tip: If you belong to a group with special health needs—such as children, pregnant or breastfeeding women, or people with chronic illnesses—always check with a healthcare provider before using products with artificial sweeteners.
Here is a summary of who should avoid or limit artificial sweeteners:
- Children: Should not consume large amounts; focus on milk, juice, and water.
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: Should limit or avoid due to unknown long-term effects.
- People with diabetes: Can use within safe limits, but should consult a healthcare provider.
- Anyone with allergies or sensitivities Should read labels and avoid products that cause symptoms.
You can make the best choice for your health by staying informed and talking with your doctor. Labels on drinks like Coke Zero can help you track what you consume. If you have concerns, moderation is always a safe strategy.
Comparison with Other Sodas

When you look at sodas on the shelf, you might wonder how Coke Zero compares to Diet Coke, Regular Coke, and other diet sodas. The main difference comes down to the sweeteners and how they affect taste, health, and nutrition.
Diet Coke
Diet Coke and Coke Zero both use artificial sweeteners, but their formulas are not identical. Diet Coke uses aspartame as its only sweetener. Coke Zero, on the other hand, blends aspartame with acesulfame potassium (Ace-K). This blend helps Coke Zero mimic the taste of regular Coke more closely. You may notice a slight difference in aftertaste between the two. Some people find Diet Coke has a lighter, crisper flavor, while Coke Zero tastes bolder and more like classic Coke.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Aspect | Diet Coke | Coke Zero |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Sweeteners | Aspartame, Ace-K | Aspartame, Ace-K |
| Acids Present | Phosphoric acid, Citric acid | Phosphoric acid only |
| Calories (per 12 oz) | 0 | 0 |
| Tooth Enamel Erosion | Slightly higher | Lower |
Note: Diet Coke contains citric acid, which can cause more tooth enamel erosion than the phosphoric acid found in Coke Zero. Studies show Diet Coke may erode enamel faster.
Both drinks have zero calories and no sugar. Research shows mixed results on weight loss and health risks. Some studies link high intake of artificially sweetened drinks to increased risk of diabetes and heart disease, but the evidence is not clear-cut. Aspartame, found in both, is classified as possibly carcinogenic, but large studies have not found a strong link to cancer.
Regular Coke
Regular Coke stands apart because it uses sugar (or high-fructose corn syrup) as its sweetener. This gives it a higher calorie count and a different taste profile. Sugar also acts as a preservative in Regular Coke. If you choose Regular Coke, you get about 140 calories and 39 grams of sugar per 12-ounce can. This sugar content can raise your blood sugar quickly and add to your daily calorie intake.
| Beverage | Sweetener Composition | Calories (per 12 oz) | Sugar (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Coke | Sugar, Glucose-Fructose | 140 | 39 |
| Coke Zero | Aspartame, Acesulfame Potassium | 0 | 0 |
Switching from Regular Coke to Coke Zero can help you cut calories and sugar. The sweetener in Coke Zero allows you to enjoy a similar taste without the extra calories.
Other Diet Sodas
Many other diet sodas use a mix of artificial sweeteners. Some use sucralose, some use aspartame, and others use Ace-K or blends. Each sweetener has a unique taste and aftertaste. For example, sucralose does not activate the brain’s reward centers like sugar, which may increase appetite and cravings. Some studies suggest that artificial sweeteners can change your gut bacteria or affect your metabolism, but results are mixed.
- Diet sodas with sucralose or Ace-K may taste sweeter or have a different aftertaste.
- Some brands use blends to mask bitterness and create a more sugar-like flavor.
- Health outcomes from drinking diet sodas vary. Some research shows modest weight loss, while other studies link high intake to increased risk of diabetes or heart disease.
Tip: If you want to avoid sugar but still enjoy soda, try different brands to find the taste you like best. Always check the label for the sweeteners used.
When you compare sodas, focus on the sweetener blend, taste, and your health goals. Coke Zero’s combination of aspartame and Ace-K sets it apart from Diet Coke and Regular Coke, giving you a sugar-free option that closely matches the classic cola flavor.
Consumer Tips
Choosing
When you select a beverage like Coke Zero, you make a choice that affects your health and taste preferences. Many factors influence your decision. Studies show that age, gender, and education can shape your preference for drinks with artificial sweeteners. For example, research found that women are more likely to choose beverages with artificial sweeteners, even after adjusting for age and education. Your taste preferences also change over time. Some people adapt to the sweetness level in diet sodas, while others prefer less sweet options after repeated exposure.
You should consider the potential health impacts of artificial sweeteners. A large review of studies links artificially sweetened beverages to higher risks of obesity, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease. Some experimental studies suggest that sweeteners like sucralose and saccharin may affect your glucose tolerance and gut health. Although these studies have limitations, they highlight the importance of making informed choices.
- Key points to consider when choosing:
- Check the ingredient list for types of sweeteners.
- Think about your health goals and any medical conditions.
- Pay attention to how your body responds to different drinks.
- Consider demographic factors, as preferences may vary by age and gender.
Tip: Read labels carefully and stay updated on new research to make the best choice for your needs.
Moderation
You can enjoy Coke Zero and similar drinks safely by following recommended intake levels. The World Health Organization sets an acceptable daily intake (ADI) for aspartame at 40 mg per kilogram of body weight. This guideline means you can drink these beverages without concern if you stay within the limit. The European Food Safety Authority also provides ADI values for other sweeteners.
| Body Mass Category | Aspartame ADI (mg/day) | Acesulfame-K ADI (mg/day) |
|---|---|---|
| Child (30 kg) | 1200 | 270 |
| Adult (50 kg) | 2000 | 450 |
| Adult (70 kg) | 2800 | 630 |
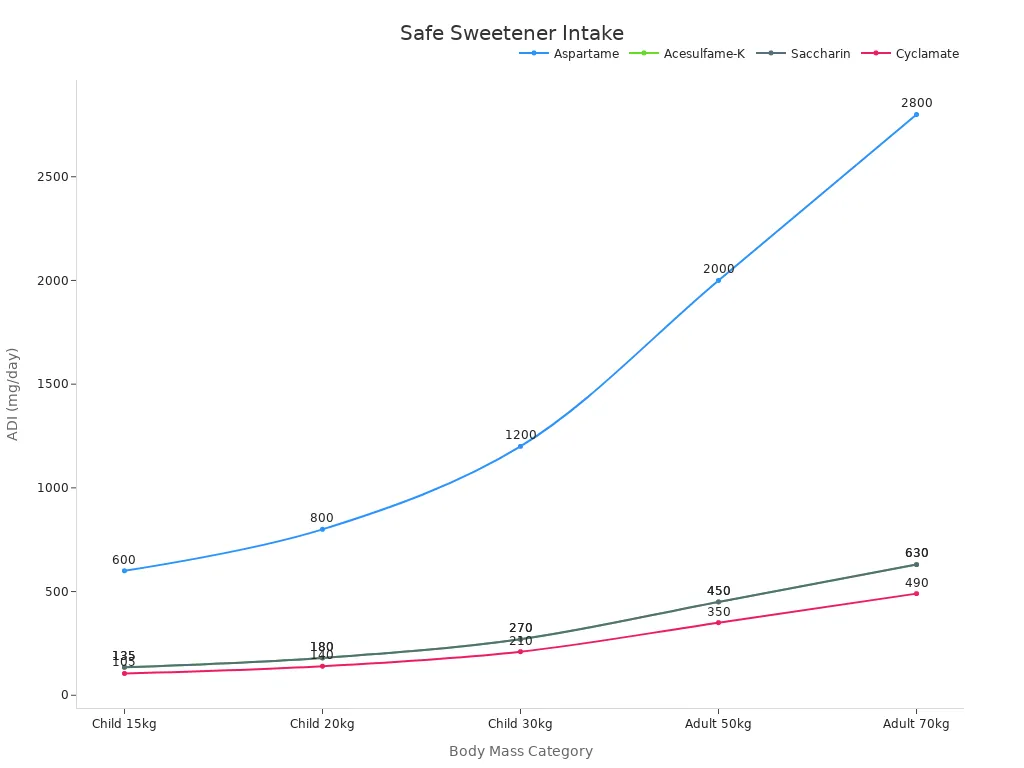
You should remember that moderation is key. Drinking large amounts of artificially sweetened beverages may increase health risks, even if you stay within the ADI. Some studies suggest possible links to weight gain and metabolic changes, but more research is needed.
Note: Try to balance your intake of diet sodas with water and other healthy drinks.
Alternatives
You have many options if you want to reduce or avoid artificial sweeteners. Several brands offer sodas sweetened with natural alternatives like stevia. For example:
- Ale 8 One Zero Sugar: Ginger ale with no aspartame, no calories, and a short ingredient list.
- Zevia: Sodas sweetened with stevia, zero calories, and no artificial dyes.
- Green Cola: Uses stevia and natural caffeine, sugar-free, and aspartame-free.
- Virgil’s: Known for traditional ingredients and natural flavors.
Some people experience headaches or mood changes with aspartame. If you notice these effects, you may want to try drinks without it. Research shows that replacing sugar-sweetened beverages with water or drinks using non-nutritive sweeteners can help with weight management and lower blood pressure. However, water remains the healthiest choice for hydration.
Tip: Explore different brands and flavors to find what works best for your taste and health goals.
You now know that the sweetener in Coke Zero combines aspartame and acesulfame potassium to deliver a sugar-free, calorie-free cola taste. Both sweeteners are FDA-approved and considered safe for moderate consumption.
- These sweeteners do not raise blood sugar or insulin levels, making them suitable for diabetics.
- The National Cancer Institute finds no clear evidence linking them to cancer or serious health risks.
- Using Coke Zero can help you reduce sugar and calorie intake.
Choose moderation and read labels to make informed choices for your health.
FAQ
What sweeteners does Coke Zero use?
You find aspartame and acesulfame potassium in Coke Zero. These artificial sweeteners give you a sweet taste without sugar or calories.
Are the sweeteners in Coke Zero safe?
You can safely consume aspartame and acesulfame potassium within recommended limits. The FDA and other health agencies approve both for use in foods and drinks.
Does Coke Zero raise blood sugar?
You do not see a rise in blood sugar after drinking Coke Zero. These sweeteners do not affect glucose levels, making Coke Zero suitable for people with diabetes.
Can children drink Coke Zero?
You should limit or avoid giving Coke Zero to children. Experts recommend that kids focus on water, milk, or natural juices for better nutrition.
Does Coke Zero help with weight loss?
You may lose weight if you replace sugary drinks with Coke Zero. Studies show that calorie-free sweeteners can help reduce daily calorie intake.
Can pregnant women drink Coke Zero?
You should talk to your doctor before drinking Coke Zero during pregnancy. Some experts suggest limiting artificial sweeteners because the long-term effects remain unclear.
Why does Coke Zero taste different from Diet Coke?
You notice a different taste because Coke Zero uses a blend of aspartame and Ace-K, while Diet Coke uses only aspartame. This blend gives Coke Zero a flavor closer to regular Coke.
Are there natural alternatives to Coke Zero?
You can try sodas sweetened with stevia or monk fruit. Brands like Zevia and Green Cola offer options without artificial sweeteners.



